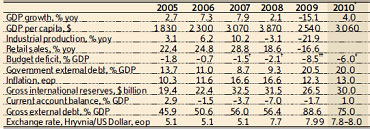
Ukraine Macroeconomic Situation: June 2010
- Real sector data showed acceleration of economic activity in April. In May, however, the external environment started to deteriorate.
- Retail trade turnover grew by 1.1% yoy, indicating that domestic consumption has started to revive.
- The state budget deficit notably widened in May on the back below-target revenues and high expenditures.
- During May-June, the government negotiated a new loan program with the IMF. At the beginning of July, a staff-level agreement was reached.
- In June, government authorities initiated tax reform in the country.
- Consumer price index growth declined to 8.5% in May.
- On June 8th, the NBU reduced its discount rate by 0.75 percentage points to 9.5% to stimulate sluggish credit activity.
- Ukraine’s Balance of Payments notably improved during April-May, contributing to foreign exchange market stability and replenishment of NBU international reserves.
A favorable external environment kept supporting Ukraine’s economic recovery. Industrial production grew by 12.6% yoy over January-May 2010, led by export-focused machine-building, chemicals and metallurgy. At the same time, in May 2010 economic activity cooled somewhat in response to easing world commodity prices. However, despite continued price corrections, their current levels remain comfortable for economic recovery in Ukraine to continue. In addition, May’s real sector data indicated noticeable improvement in domestic demand.
At the beginning of July, a staff-level agreement with the IMF was achieved on a new loan program of up to $14.9 billion for 2.5 years.
During April-May 2010, Ukraine made significant progress in reducing inflation. Annual consumer price index growth fell to 8.5% in May 2010 on the back of still weak domestic demand, a delay in utility tariff increases, correction of world commodity prices and favorable developments on the foreign exchange market.